How UVC Lights Work
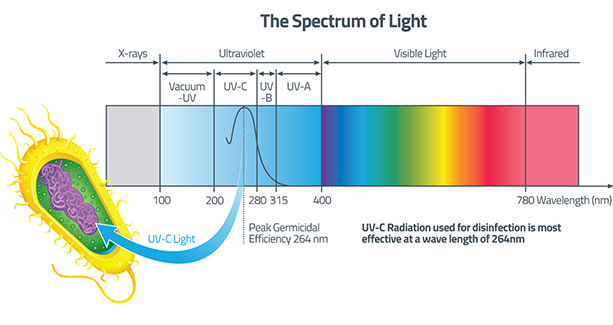
UV-C is one of many electromagnetic frequencies emanating from the sun. Like other of these waveforms, its properties are unique to its wavelength. To synthesize this frequency, a glass tube is evacuated and refilled with argon at far below atmospheric pressure. Added to this is a small amount of mercury. When the mixture is energized (excited) it creates a glowing plasma of electrons that pass through the mercury vapor. As they strike mercury atoms, a mercury electron is liberated at a frequency representative of mercury’s spectral line, which is 253.7nm. The dominant emission (>90%) from these lamps is UV-C energy. The “C” frequency of the electromagnetic UV family has, amongst other things, germicidal effects
We’re exposed to parts of the UV spectrum while outdoors. Generally, excessive UV exposure can produce adverse effects depending on wavelength, type and duration, and UV response differences between individuals. The three basic wavelengths:
- UV-C – includes the germicidal wavelength of 253.7nm and is used for air and water disinfection. Human overexposure causes temporary skin redness and harsh eye irritation, but no permanent damage, skin cancer, or cataracts.
- UV-B – is a narrower but more dangerous band of UV. Prolonged exposure has been associated with skin cancer, skin aging, and cataracts (clouding of the lens of the eye).
- UV-A – is more predominant outdoors than the other two. It helps to tan our skin and is used in medicine to treat certain skin disorders. It is generally a harmless wavelength. UVA, B and C will damage collagen fibers and accelerate skin aging. Generally, UVA is least harmful; UVB contributes to DNA damage and cancer. It penetrates deeply but does not cause sunburn. Because of no reddening (erythema) it cannot be measured in SPF testing. There’s no good clinical measurement of UVB blocking, but it is important that sunscreens block both UVA and B. UVC however, penetrates superficially and has not been associated with long term tissue effects.
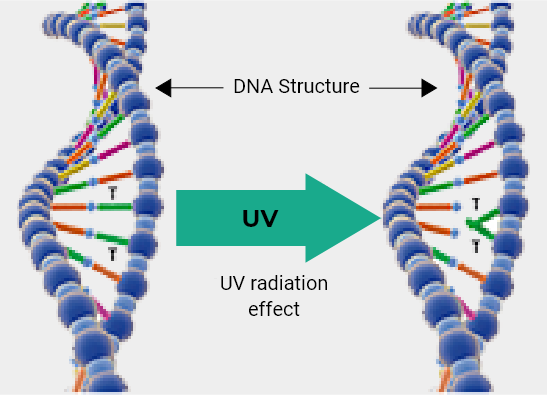
Microorganisms are simple organic structures that readily absorb the UV-C wavelength, causing photo-disassociation (destruction). A microbes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid, is first to be adversely effected due to its weaker molecular bonds. In hundredths of a second it suffers irreparable damage. The subsequent loss of genetic instructions causes cell death and/or the inability to replicate, rendering them harmless. Continuous exposure causes uninterrupted degradation, such as the sun does, only significantly faster.
